Hi, I’m Yoshihiro (Yoshi)
Machine Learning Engineer
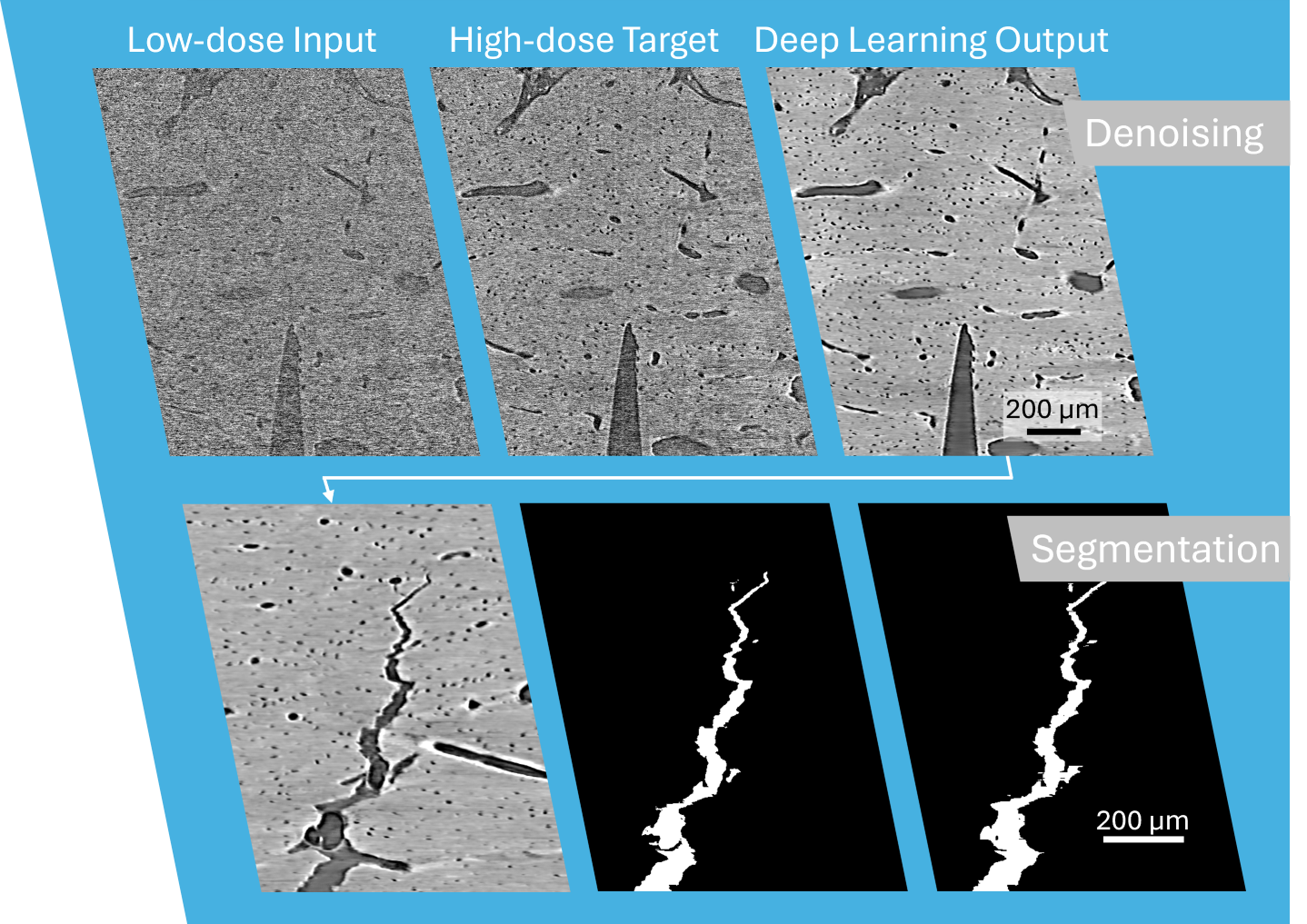
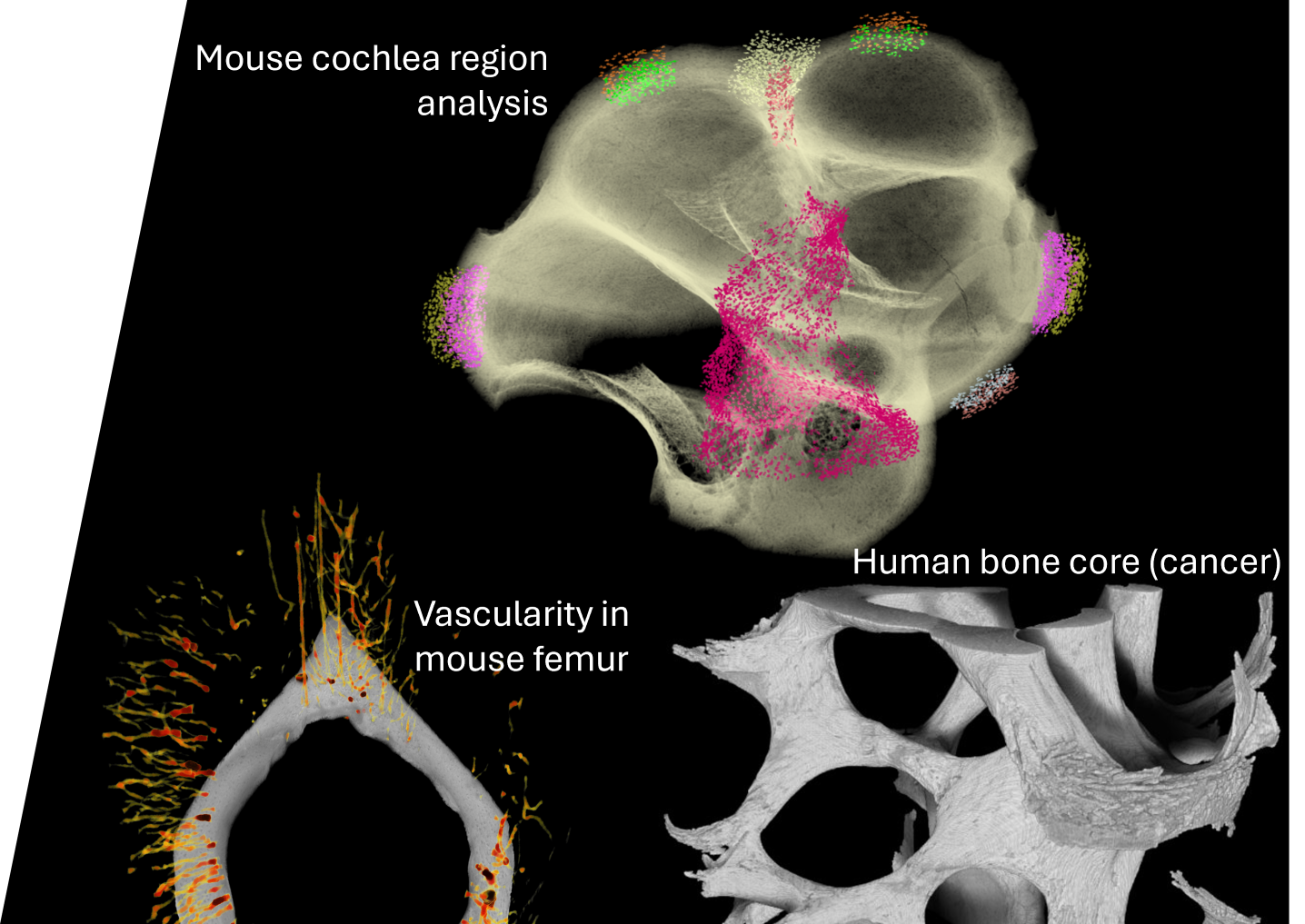
Nice to meet you! I am a graduate student using deep learning to denoise and segment images of bone in the Fracture and Fatigue of Skeletal Tissues Lab at UC San Diego. I'm graduating with my PhD in December 2024 and am looking for opportunities to continue my passion for machine learning and engineering.
Contact